
The timezones are using “Region/City” format. The system’s timezone in also written to the /etc/timezone file: cat /etc/timezone UTCĬhanging the Timezone Using the timedatectl Command #īefore changing the timezone, you’ll need to find out the long name for the timezone you want to use. The system timezone is configured by symlinking /etc/localtime to a binary timezone identifier in the /usr/share/zoneinfo directory.Īnother option to view the current system’s timezone is find the file to which the symlink points to: ls -l /etc/localtime lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 27 Dec 10 12:59 /etc/localtime -> /usr/share/zoneinfo/Etc/UTC The output below shows that the system’s timezone is set to “UTC”: Local time: Wed 19:33:20 UTC Universal time: Wed 19:33:20 UTC RTC time: Wed 19:33:22 Time zone: UTC (UTC, +0000) System clock synchronized: yes NTP service: active RTC in local TZ: no To print the current system’s timezone invoke the timedatectl without any arguments: timedatectl It is available on all modern systemd-based Linux systems including Ubuntu 20.04. Timedatectl is a command-line utility that allows you to view and change the system’s time and date. Only the root or user with sudo privileges can set or change the system’s timezone.
#Change timezone linux command line how to#
This article describes how to set or change the timezone on Ubuntu 20.04 using the command line, or through the GUI. On Ubuntu, the system’s timezone is set during the install, but it can be easily changed at a later time.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/linux-free-total-9b52e189011c451dbdce6d9f22de100a.jpg)
For example, the cron daemon uses the system’s timezone for executing cron jobs, and the timestamps in the log files are based on the same system’s timezone.
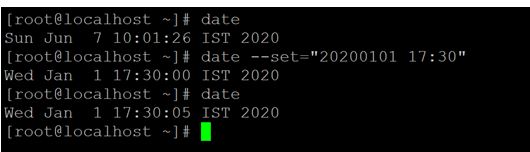
Using the correct timezone is essential for many systems related tasks and processes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
